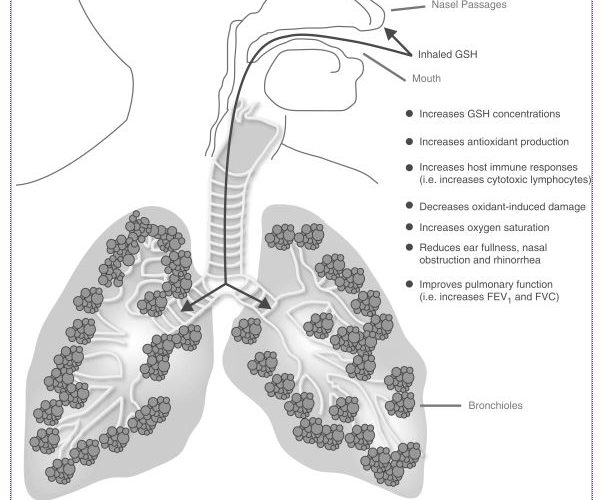
Glutathione is a major antioxidant and cellular protector found throughout the body. A high amount can be found in the lining of the respiratory tract and nasal cavities making it a useful nutrient in the treatment and management of conditions affecting the respiratory system.
Glutathione is a very simple molecule that is produced naturally all the time in your body. It is a combination of three simple building blocks of protein or amino acids – cysteine, glycine and glutamine. It is the first line of defense against oxidative stress. Poor diet, pollution, toxins, medications, stress, trauma, aging, infections and radiation all deplete your glutathione levels throughout your body.
Inhalation (nebulized or aerosolized) is the only known method that increases glutathione’s levels in the epithelial lining fluid of the respiratory tract.
GSH (reduced glutathione) inhalation is a good treatment for a variety of pulmonary diseases and respiratory related conditions. Even very serious and difficult to treat diseases yield benefits from this treatment. Conditions include:
- Acute respiratory infections
- Sinus conditions
- Recurring ear infections (chronic otitis media with effusion)
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Chronic cough
- Irritation from toxic exposure (fumes, cigarette smoke, allergens)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
The administration of GSH inhalation before and/or immediately following exercise is another potential application of this novel treatment. Exercise is a known inducer of oxidative stress leading to free radical production, which can encourage lipid peroxidation and tissue damage among individuals with deficient and/or impaired antioxidant systems.
GSH inhalation is very safe. Because many pulmonary diseases and respiratory related conditions are affected by deficient antioxidant status, poor oxygenation and/or impaired host defenses, glutathione remains an excellent choice for correcting these imbalances. In addition, glutathione is only beneficial for lung conditions when it is delivered directly to the pulmonary tissue – something that can only be achieved using a nebulizer.